What is the specialty of Renewable Energy:
Renewable energy is energy collected from renewable resources that are naturally replenished on a human time scale. They include sources such as sunlight, wind, rain, tides, waves, and underground heat. Renewable energy contracts with fossil fuels, which are used much faster than they are renewed. Although most renewables are sustainable, some are not. For example, some biomass sources are considered unsustainable at current exploitation rates.
Renewable energy often provides energy in four important areas: electricity generation, air and water heating/cooling, transport, and rural (off-grid) energy services. About 20% of human global energy consumption is renewable, including approximately 30% of electricity. About 8% of energy consumption is conventional biomass, but this is declining, and more than 4% of energy consumption is thermal energy from modern renewable sources, such as solar water heating, and more than 6% electricity.
Globally, more than 10 million jobs are associated with renewable energy industries, with solar photovoltaic cells being the largest renewable employer. Renewable energy systems are becoming more efficient and cheaper quickly, and their share of total energy consumption is increasing, with the vast majority of newly installed electricity worldwide being renewable.
Many countries around the world already have renewable energy that contributes more than 20% of their energy supply, with some generating more than half of their electricity from renewable energy sources, and national renewable energy markets are expected to continue to grow strongly in the next decade and beyond. All electricity is generated using renewable energy. Renewable energy resources are found in large geographical areas, unlike fossil fuels, which are concentrated in a limited number of countries. The deployment of renewable energy technologies and energy efficiency results in significant energy security, climate change mitigation, and economic benefits. But renewable energy sources are hampered by hundreds of billions of dollars in fossil fuel subsidies. In international public opinion polls, there is strong support for promoting renewable sources such as solar and wind energy.
While many renewable energy projects are large-scale, renewable technologies are also suitable for rural and remote areas and developing countries, where energy is often critical to human development. Because most renewable energy technologies provide electricity, renewable energy is often deployed alongside more electrification, which has many benefits: Electricity can be converted to heat, can be converted to mechanical energy at high efficiency, and is clean when consumed. In addition, electrification using renewable energy is more efficient, thus leading to significant reductions in primary energy requirements. In 2021, China accounted for nearly half of the increase in renewable electricity. In 2021, Norway, known for its hydroelectric production, consumed 45% of its total energy supply.
History of Renewable Energy Specialization:
Before the development of coal in the mid-19th century, almost all of the energy used was renewable. The earliest known use of renewable energy, in the form of traditional biomass to fuel fires, goes back more than a million years. It was not until hundreds of thousands of years later that the use of fire biomass became common. Perhaps the second oldest use of renewable energy is to harness the wind to push ships above water. This practice can be traced back to about 7000 years, to ships in the Persian Gulf and on the Nile River. From hot springs, geothermal energy has been used for bathing since the Paleolithic and for heating places since ancient Roman times. Moving to the time of recorded history, the primary sources of conventional renewable energy were human labor, animal energy, hydro, wind, windmills to crush grain, firewood, and traditional biomass.
In the 1860s and 1870s, there were already fears that civilization was running out of fossil fuels and felt the need for a better source. In 1873 Augustin Moschot wrote:
The time will come when European industry will stop finding those natural resources necessary for it. Oil springs and coal mines are not inevitable but are rapidly dwindling in many places. Will man then return to the power of water and wind? Or migrates where the most powerful source of heat sends its radiation to everyone? History will show what's coming.
In 1885, Werner von Siemens, commenting on the discovery of the photovoltaic effect in the solid-state, wrote:
In conclusion, I would like to say that, whatever the scientific significance of this discovery may be, its practical value will be no less obvious when we reflect that the supply of solar energy is limitless and inexpensive and that it will continue to flow. We were stumbled upon countless times after all the coal deposits in the land were depleted and forgotten.
Max Weber mentioned the end of fossil fuels in the closing paragraphs of his "Die protestantische Ethik und der Geist des Kapitalismus," published in 1905. The development of solar engines continued until the outbreak of World War I. The importance of solar energy was recognized in a 1911 Scientific American article: "In the distant future, natural fuels after the depletion of [solar energy] will continue to be the only means for the existence of mankind."
The theory of peak oil was published in 1956. In the 1970s, environmentalists were encouraged to develop renewable energy as an alternative to eventual oil depletion, as well as to eliminate dependence
On oil, the first electric wind turbines. Back. Solar power was always used for heating and cooling, but solar panels were very expensive to build solar farms until 1980.
Since the twenty-first century, many parts of the world have turned to renewable sources of energy from fossil fuels.
The importance of studying the specialty of Renewable Energy:
When it comes to energy resources, there's always the question of sustainability. It is important that resources provide sufficient energy to meet our needs - to heat our homes, to operate our cities, and to operate our cars. However, it is also important to consider how these resources can be used in the long term. Some resources will not be exhausted in practice. These are known as renewable resources. Renewable resources also produce clean energy, which means reducing pollution and greenhouse gas emissions, which contribute to climate change.
Energy sources in the United States evolved over time, from wood use before the 19th century to the subsequent adoption of non-renewable resources, such as fossil fuels, petroleum, and coal, which remain the dominant sources of energy today. But the land has a limited supply of these resources. Recently, the use of renewable resources has begun to increase. According to the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency, 11 percent of U.S. energy consumption came from renewable sources in 2017.
There are some challenges associated with the use of renewable resources. For example, renewable energy can be less reliable than non-renewable energy, with seasonal or even daily changes in the amount produced. However, scientists are constantly dealing with these challenges and working to improve the feasibility and reliability of renewable resources. Renewable resources include biomass energy (such as ethanol), hydro, geothermal, wind, and solar.
Biomass refers to organic matter from plants or animals. This includes wood, sewage, and ethanol (coming from maize or other plants). Biomass can be used as an energy source because this organic matter absorbs energy from the sun. This energy is released, in turn, as thermal energy in combustion.
Hydropower is one of the oldest renewable resources and has been used for thousands of years. Today, every U.S. state uses a measure of hydroelectric power. With hydroelectric power, mechanical power from flowing water is used to generate electricity. Hydroelectric power plants use the flow of rivers and streams to run turbines to run the generator, and to release electricity.
Geothermal energy comes from the heat generated deep in the Earth's core. Geothermal reservoirs can be found at tectonic plate boundaries near volcanic activity or deep Earth. Geothermal energy can be harnessed by drilling wells to pump hot water or steam into the power plant. This power is then used for heating and electricity.
Renewable Energy courses:
- Advanced battery and fuel cell technologies
- Power systems technology
- Engineering management, economics, and risk analysis
- Multidisciplinary cluster project
- Renewable and alternative energy
- Smart Network Fundamentals
Fields of work for the Renewable Energy major:
- Contractor/Electrician
- Green Engineering
- Sustainable agriculture
- Environmental Adviser
- Mechanic
- architecture and design
Best Universities for Renewable Energy in Turkey:
- İstanbul Bahcesehir University
 FR
FR AR
AR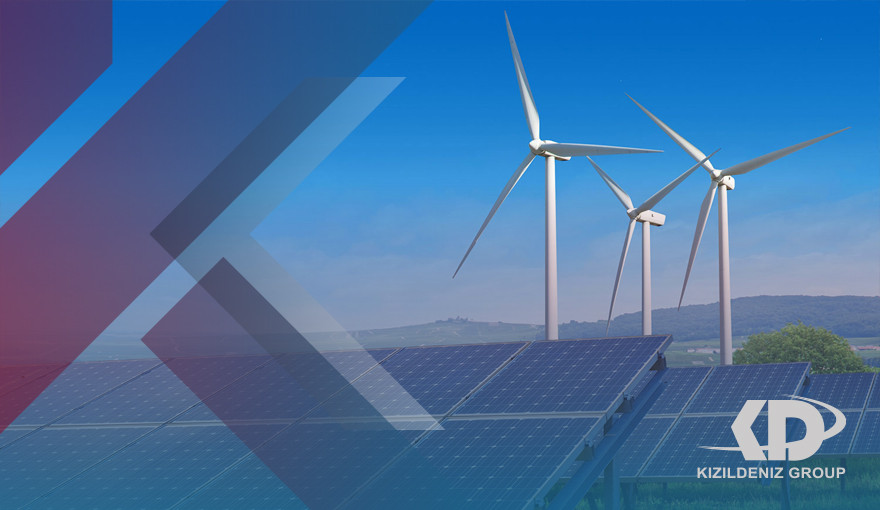
 Next one
Next one