What is the specialty of Technology and Innovation:
Technology ("craft science," from Greek, technology, "art, skill, craftsmanship"; logia) is the sum of many techniques, skills, methods, and processes used to produce goods or services or to achieve objectives, such as scientific research. Technology can be defined by techniques, processes, and the like, or it can be included in machines to allow operation without detailed knowledge of their work. Systems (such as machines) that apply technology by taking inputs, changing them according to the use of the system, and then producing a result referred to as technology systems or technology systems.
The simplest form of technology is the development and use of basic tools. The invention of stone tools formed in prehistoric times, followed by the discovery of fire control, increased food sources. The later Neolithic Revolution expanded this, quadrupling the available power from the region. The invention of the wheel helped humans travel and control their environment.
Developments in historical times, including the printing press, telephone, and the Internet, have reduced physical barriers to communication and allowed humans to interact freely on a global scale.
Technology has many effects. It helped develop more advanced economies (including today's global economy) and allowed the emergence of a recreational class. Many technological processes produce unwanted by-products known as pollution and drain natural resources at the expense of the Earth's environment. Innovations have long influenced the values of society and raised new questions about the ethics of technology. Examples include the emergence of the notion of efficiency in terms of human productivity and the challenges of bioethics.
Philosophical discussions have arisen about the use of technology, with disagreements over whether technology improves or exacerbates the human condition. Neo-amity, radio primality, and similar retrograde movements criticize the spread of technology, arguing that it harms the environment and alienates people; proponents of ideologies such as post-humanism and technological progress see continued technological progress as beneficial to society and to the humanitarian situation.
History of Technology and Innovation Specialization:
Paleolithic (2.5 mm amp - 10 ka)
Primitive Helicopter
More information: Prehistoric Technology Scheme
The use of tools by early humans was partly a process of discovery and evolution. Early humans evolved from a type of human feeding on two feet, with a brain mass of nearly one-third of modern humans. The use of tools has remained relatively unchanged for most of human early history. Almost 50000 years ago, tool use and a complex set of behaviors emerged, many archeologists believe to be linked.
With the emergence of a completely modern language.
Stone Tools
Hand axes of the Acheulian period
Campfire often used to cook food
Point Clovis, performed by peeling pressure
Metal balustrade, estimated to be 1600 to 1700 peeled with pressure
Humans began using primitive stone tools millions of years ago. Early stone tools were little more than a broken rock, but almost 75000 years ago, compression peeling provided a means of doing more accurate work.
Main article: Control of fire by early humans
The discovery and use of fire, a simple source of energy with many deep uses, was a turning point in the technological development of humanity. The exact date of its discovery is unknown. Evidence of burning animal bones in the cradle of the human race indicates that fire domestication occurred 1 million years ago; Scientific consensus indicates that the human erect has controlled fire by 500 to 400.
kilowatt. Their food is to increase their digestibility, improve their nutritional value and increase the number of foods that can be eaten.
Clothing and shelter
Other technological developments during the Paleolithic era were clothing and shelter. Both techniques cannot be exactly adopted, but they were key to the progress of mankind. As the Paleolithic Age progressed, housing became more complex and elaborate; As early as 380ka, humans were building temporary wooden huts. Clothing, adapted from fur and animal skins caught, helped humanity expand into cooler areas; Humans began migrating from Africa by 200 ka and to other continents such as Eurasia.
Modern Stone Age during classical antiquity (10 ka-300 m)
A collection of modern Stone Age artifacts, including bracelets, ax heads, azamel, and polishing tools
The technological rise of man began in earnest in what is known as the Neolithic ("Neolithic"). The invention of polished stone axes was a major advance that allowed large-scale deforestation to create plantations. The use of polished stone axes increased significantly in the Modern Stone Age but was originally used in the former Middle Stone Age in some areas such as Ireland. Carry it, as the Bedouins should. In addition, children can contribute to crop breeding more easily than they can to the fishing economy.
With this increase in population and availability of employment, there has been an increase in the specialization of work. What led to progress from early Neolithic villages to the first cities, such as Uruk, and the first civilizations, such as Sommer, are not known in particular; However, the emergence of increasingly hierarchical social structures and specialized employment, trade, and war between neighboring cultures, and the need for collective action to overcome environmental challenges such as irrigation, are believed to have played a role.
Metal Tools
Continuous improvements led to the furnace and vents and, for the first time, provided the ability to fuse and form the original gold, copper, silver, and lead metals found in relatively pure form in nature. The advantages of copper instruments soon became apparent over the stone, bone, and wooden tools of early humans, and the original copper may have been used since about the beginning of the Modern Stone Age (about 10 Ka). There is no natural copper in large quantities, but copper ores are very common and some produce metal easily when burned in wood or coal fire. In the end, metalwork led to the discovery of alloys such as bronze and yellow copper (around 4000 BC). The first uses of iron alloys such as steel date back to about 1800 BC.
Energy and transport
The wheel was invented around 4000 BC.
Main article: Transport history in the meantime, humans were learning to harness other forms of energy. The first known use of wind power is sailing ships. The earliest record of a sailing ship is that of a Neely boat dating from the 8th millennium BC. Since prehistoric times, Egyptians may have used the power of the annual flood of the Nile River to irrigate their land, and gradually learned to organize much of it through deliberately built irrigation canals and "fishing" basins.
The importance of studying the specialty of Technology and Innovation:
Functional specialization is the degree to which the overall mission of an organization is divided into smaller component parts. The administrative division, on the other hand, is the clustering of posts according to some logical arrangements. Impact of these variables on functional satisfaction
Among the library staff was the focus of this study. It was a descriptive search design.
It was adopted while using the scanning method to extract information from respondents for this purpose.
Fifty (50) copies of the questionnaires were distributed with 30 structured questions among participants.
Nimble Adedipe Library staff, Federal University of Agriculture, Abeokuta, and 45 (90%)
It's been returned. The questionnaire sought information on the demographic and function of respondents.
specialization, departments, and the effects of functional and departmental specialization on the job satisfaction of respondents. The data analysis was based on 42 questionnaires where 3 questionnaires were not fit for use. One of the results of this study is that the majority of library staff sampled were fully satisfied with their current area of specialization. Although the indexing section was seen as the most boring section to work in any library, this may not be true after all, since then an introduction has been made to indexing and classifying online versions allowing for interaction with them.
Technology and Innovation courses:
- Mathematics
- Humanities
- Science
Best Universities for Technology and Innovation in Turkey:
- İstanbul Bahcesehir University
 FR
FR AR
AR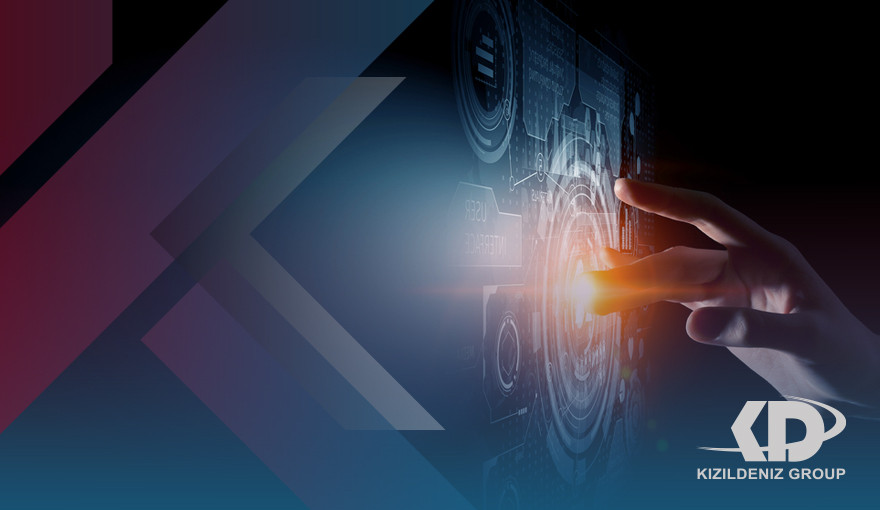
 Next one
Next one