What is the specialty of Information Security Technology:
Computer security, cybersecurity, or information technology security (IT security) is the protection of computer systems and networks from detecting information, stealing, or destroying their devices, software, or electronic data, as well as from disrupting or misdirecting services they provide. This area is becoming increasingly important due to the continued expansion of reliance on computer and Internet systems and wireless network standards such as Bluetooth and Wi-Fi, and the growth of "smart" devices, including smartphones, televisions, and various devices that make up the "Internet of Things." Cybersecurity is also an important challenge in the modern world, given its complexity, both in terms of political use and technology.
History of Information Security Technology Specialization:
Since the arrival of the Internet and with the digital transformation that has begun in recent years, the concept of cybersecurity has become a familiar theme in our professional and personal lives. Cybersecurity and cyber threats have been constant over the past 50 years of technological change. In the 1970s and 1980s, computer safety was mainly restricted to academia until the advent of the Internet, as computer viruses and network intrusions began to emerge as communication increased. Following the spread of viruses in the 1990s, the first decade of the twenty-first century saw the institutionalization of cyber threats and cybersecurity. Finally, since 2010, large-scale attacks and government regulations have been emerging. The April 1967 session organized by Willis Weir at the Spring Justice Computer Conference, and the subsequent publication of the Ware Report, were founding moments in the history of the computer safety field. Weir's work extended to the intersection of material, cultural, political, and social concerns. The 1977 NIST publication "CIA Socialization" presented confidentiality, integrity, and availability as a clear and simple way to describe key safety objectives. While still appropriate, several detailed frameworks have been proposed since then. However, in the 1970s and 1980s, there were no serious computer threats because computers and the Internet were still evolving, and security threats were easily identified. Threats often come from harmful insiders who have obtained unauthorized access to sensitive documents and files. Although harmful programs and network violations existed during the early years, they were not used for financial gain. However, by the second half of the 1970s, established computer companies such as IBM began offering commercial access control systems and computer safety software products.
It began with Creeper in 1971. Creeper was an experimental computer program written by Bob Thomas at BBN. It's the first computer worm.
In 1972, the first antiviral program called Reaper was created. It was created by Ray Tomlinson to move through ARPANET and delete the mobile virus Creeper.
Between September 1986 and June 1987, a group of German infiltrators made the first documented case of cyber espionage. The group hacked the networks of defense contractors, universities, and U.S. military bases and sold the information collected to the Soviet KGB. The group was led by Marcus Hess, who was arrested on 29 June 1987. He was convicted of espionage (together with two conspirators) on February 15, 1990.
In 1988, one of the first computer worms, called the Morris worm, was distributed online. I've gained a lot of attention from the mainstream media.
In 1993, Netscape began developing the SSL protocol, shortly after the National Center for Supercomputing Applications (NCSA) launched Mosaic 1.0, the first web browser, in 1993. Netscape version 1.0 of SSL was ready in 1994 but was never released to the public due to several serious security gaps. These weaknesses included reboot attacks and a vulnerability that allowed hackers to change the non-encrypted communications sent by users. However, in February 1995, Netscape launched version 2.0.
The importance of studying the specialty of Information Security Technology:
Sensitive data is one of the most important assets of an enterprise, so it makes sense to prioritize its security. Information security is the "practice of preventing unauthorized access, use, disclosure, disruption, modification, inspection, registration or destruction" of sensitive records.
This exercise plays four important roles:
Protects the Organization's ability to operate.
Allows for the safe operation of applications applied to enterprise information technology systems.
Protects data collected and used by the organization.
It protects the technology used by the Organization.
challenges
In an increasingly interdependent environment, information is exposed to an increasing and diverse number of risks.
Threats such as malicious code, hacking on a computer, and denial-of-service attacks have become more common, ambitious, and complex, making it more challenging to implement, maintain and update information security in an institution.
How do you move on?
The implementation of information security in an enterprise can protect the assets of the technology and information it uses by preventing, detecting, and responding to threats, both internally and externally.
Senior management and information technology are both responsible for the Organization's information security strategy, although this function in smaller institutions is likely to deal with risks, safety, data and compliance, and information security and information technology managers and managers (sometimes this is just one person).
To support the information security strategy, it is important to improve staff awareness of information security issues through training and initiatives. Organizations also need to enforce and regularly review their own information safety policies to meet safety requirements.
Threats and vulnerabilities must be assessed and analyzed. This means establishing and implementing control measures and procedures to reduce risks, and auditing to measure the performance of controls. Another key part of your information security strategy and project is compliance with GDPR (General Data Protection Regulation). CyberCompany's aim is to make data protection, cybersecurity, information security, and risk management straightforward and affordable for all. Drawing on our years of experience in developing and disseminating risk management tools and services, our products reduce the complexity of your implementation project. CyberCompany guides enterprises through electronic risk control, privacy, and compliance. It is designed for risks and safety, data and compliance, and IT and information security specialists working in SMEs whose privacy and cyber risk management is critical.
Developed for:
Identify data security risks and process them quickly before they become critical concerns.
Map data flow in minutes as key data processing risks are reported.
Do DPIA as an expert, saving time, money, and resources.
Reduce errors and improve the completeness of risk management processes.
Follow the processes step by step and the guidance included to ensure compliance.
It also contains an interactive and intuitive information board that gives you a real-time overview of your project that you can customize to see what's important to you.
Information Security Technology courses:
- Analysis of baseline data.
- Basic or introductory programming.
- Cyber defense.
- Cyber threats.
- Basic safety design principles.
- Basics of information assurance.
- An introduction to encryption.
- Components of information technology systems.
Fields of work for the Information Security Technology major:
- Web Development
- Management of Internet and Computer Network Systems
- Database Responsible Position
- Information technology adviser
- Forensic Investigation of Computer Software Engineering
- Design of data models
- Developing smartphone applications
- Project management in information design
- Website design
 FR
FR AR
AR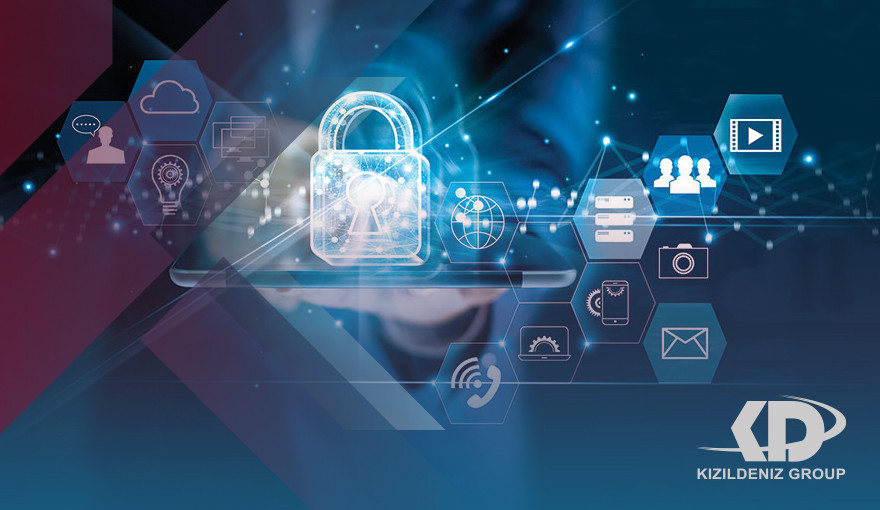
 Next one
Next one